Venezuela Closes Embassies In Norway And Australia
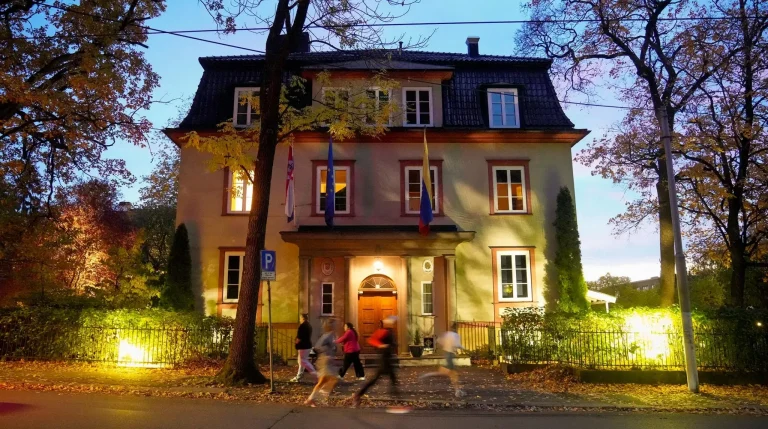
On Monday, Venezuela’s Foreign Ministry announced that it has begun the first phase of a comprehensive restructuring of its foreign service, ordering the closure of its embassies in the Kingdom of Norway and Australia.
“As part of the strategic reallocation of resources, the closure of the embassies in the Kingdom of Norway and Australia has been ordered,” the ministry said in a statement.
Venezuela explained that bilateral relations and consular assistance for the Venezuelan community in Norway and Australia “will be efficiently addressed through concurrent diplomatic missions, the details of which will be announced in the coming days.”